BIO-ECOLOGICAL DRAINAGE SYSTEM (BIOECODS) – A SUSTAINABLE GREEN UNIVERSITY DRAINAGE SYSTEM
Introduction
Constructed in 2001, the Bio-Ecological Drainage System (BIOECODS) is a national pilot project located at the Engineering Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM Engineering Campus), Penang. It represents a drainage system to restore natural environment while maintaining river flow and controlling ground subsidence through an innovative and sustainable method. The concept of the BIOECODS is based on Sustainable Urban Drainage System (SUDS) or Best Management Practices (BMPs), namely the "Control-at-Source" approach, integrated into urban planning and designed to achieve multiple objectives. By integrating green stormwater components (swales, dry ponds, wetlands, wet ponds) with the green area and landscape, the BIOECODS will also enhance the aspect of a “healthy campus”. Through the construction of the BIOECODS in newly developed areas, several water-related conundrums including rapid flooding, river pollution, and scarcity of water during dry seasons which have afflicted Malaysia will likely be overcome. The BIOECODS in USM is a national pilot project and can be seen as a prototype for developing new urban areas. This project meets the Urban Stormwater Management Manual for Malaysia (MSMA) requirement, which was launched in 2000 by the DID to manage and control the quantitative and quality runoff of stormwater at its source. The implementation of the BIOECODS will also help maintain the downstream waterway, i.e., River Kerian, in a natural environment.
The concept of quantity control in stormwater runoff applies engineering elements including infiltration, storage, and flow attenuation. The infiltration and storage component helps to attenuate the runoff flow and improve the runoff water quality through the treatment process. Removal of pollutants from the stormwater runoff can be achieved through applying best management practices from the source to the river. Treated runoff can also be stored and detained in the designed pond such as the wet pond and recreational pond for domestic use.
The BIOECODS includes a series of components from upstream to downstream, namely grass swale, dry pond and ecological pond (wet pond, detention pond and recreational pond) (Fig. 1(a)). Fig. 1 (b) shows the schematic layout of the BIOECODS.
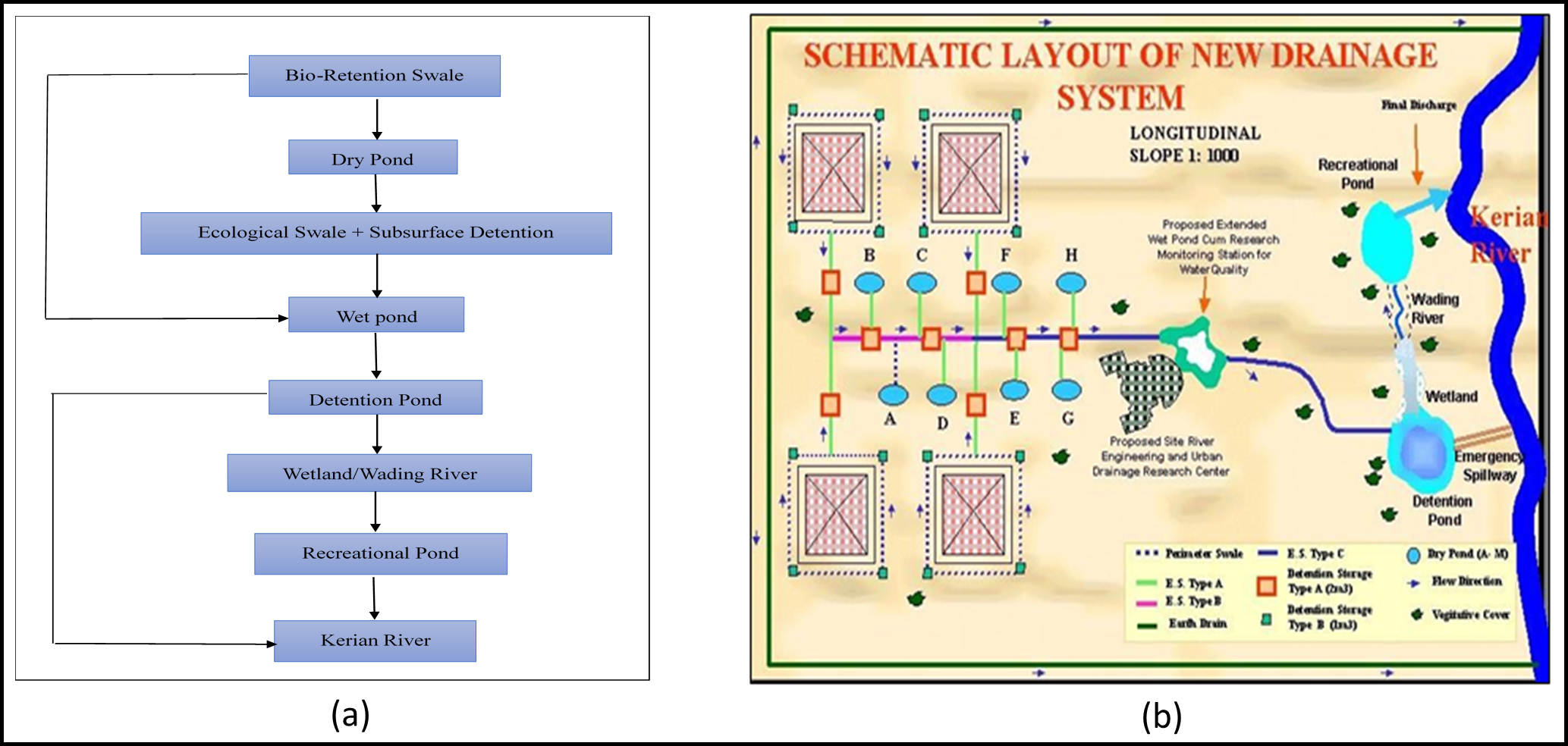
Fig. 1 shows (a) Flow concepts of BIOECODS, (b) Schematic Layout of BIOECODS
SUSTAINABILITY ASPECTS OF BIOECODS
The Bio-Ecological Drainage System (BIOECODS) offers several advantages including:
- Attenuation of peak flow
- Alternative water resources for domestic use
- Treatment of stormwater runoff
- Increase in groundwater
- Increased concentration of dissolved oxygen
- Adds aesthetic value and provides a green surrounding area
- Increase the aquatic life population
BIOECODS: Water Quality Standards for Protecting Ecosystems and Health
The BIOECODS system adheres to the Urban Stormwater Management Manual for Malaysia (MSMA), which outlines comprehensive guidelines to control both the quantity and quality of stormwater runoff at its source. MSMA promotes a control-at-source approach, ensuring that runoff is managed before it reaches larger bodies of water. This approach helps in mitigating pollution and preserving water resources in urban settings.
In terms of water quality, the National Water Quality Standards (NWQS) for Malaysia plays a crucial role in regulating the water discharged from the BIOECODS system, particularly before it enters the Kerian River. The system is designed to meet Class II A/B standards of the NWQS, which ensure that the discharged water is safe for the protection of aquatic ecosystems, wildlife, and human health.
Class II A/B of the NWQS is generally applied to water bodies that require a balance between natural habitat conservation and human activities. The standards stipulate specific thresholds for key water quality parameters, including dissolved oxygen (DO), total suspended solids (TSS), biochemical oxygen demand (BOD), and chemical oxygen demand (COD), all of which are crucial indicators of the ecological health of the water.
By meeting these standards, BIOECODS not only enhances water quality but also supports biodiversity conservation by ensuring that water discharged into the environment is free from harmful pollutants. The system also incorporates constructed wetlands and detention ponds, which naturally treat stormwater through biological filtration, further contributing to improved water quality. This natural filtration mimics the functions of natural ecosystems, ensuring that the water discharged from the system aligns with Malaysia's environmental protection efforts.
In Malaysia, the implementation of MSMA and NWQS helps align urban water management practices with the sustainability goals of the country, reducing the risk of water pollution while maintaining the natural integrity of aquatic ecosystems. The integration of these guidelines within BIOECODS demonstrates a proactive approach to addressing the environmental challenges posed by urbanization, especially in the context of water resource management and ecosystem protection.
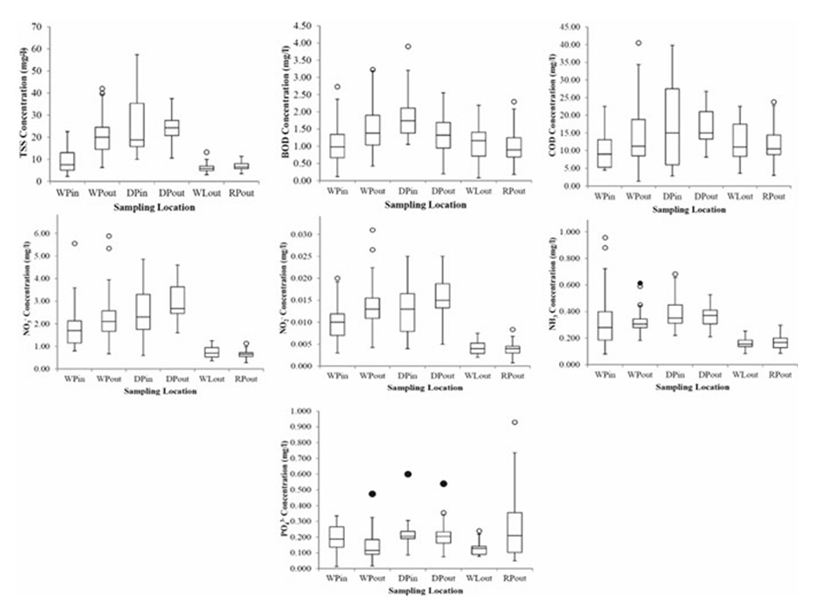
Water quality trend of nutrients in BIOECODS (TSS, BOD, COD, NO2−,NH3−,NO3− and PO4) (Beh, 2014)


Quality of the water at the end of the BIOECODS system
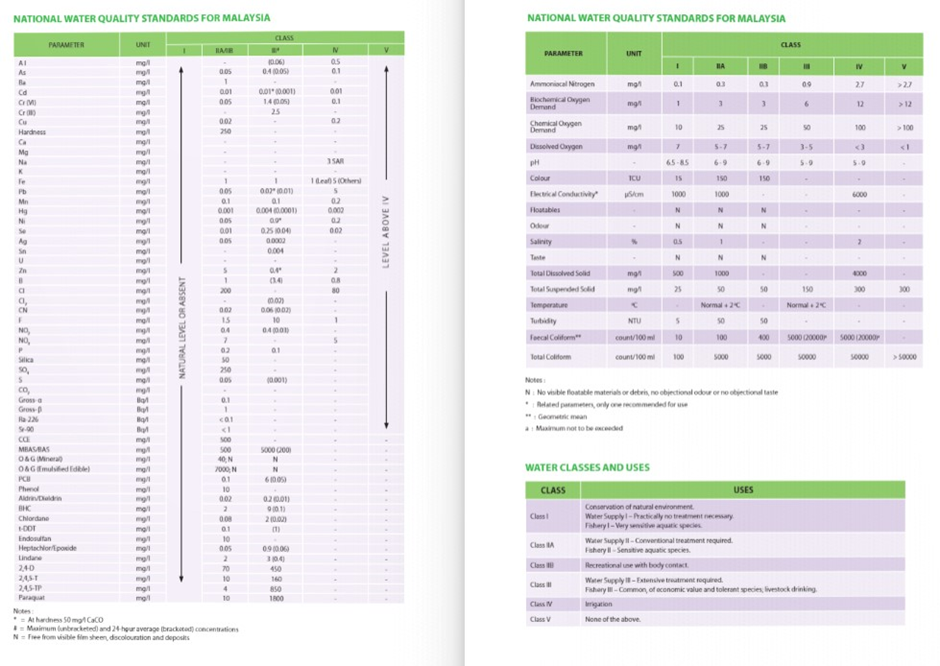
National Water Quality Standards for Malaysia
LIST OF BIOECODS PROJECTS IN MALAYSIA
Professor Dato Dr. Nor Azazi started and led the River Engineering and Urban Drainage Research Centre (REDAC) in 2001. He is the project leader for all BIOECOS projects. Out of 11 states on the Peninsula of Malaysia, REDAC covered eight states. Since the inception of BIOECODS, almost 20 projects have been implemented throughout Peninsular Malaysia, mainly for government building development projects. BIOECODS has received overwhelming responses from developers, engineers, stakeholders, regulators, planners, designers, etc.
- BIOECODS at Engineering Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia (Malaysian Pilot Project for the country)
- Seri Mutiara, Pulau Pinang – Park Lawn
- Padang Seri Mutiara, Pulau Pinang – Nursery Plantation
- Kolej Universiti Automotif Antarabangsa (IUCAM), Pekan, Pahang Darul Makmur
- Student Village, Kolej Universiti Automotif Antarabangsa (IUCAM), Pekan, Pahang Darul Makmu
- Proposed Construction and Completion of Freshwater Laboratory Complex, Tasik Chini, Pekan, Pahang Darul Makmur
- Pembangunan Tanah Wakaf Khas, Kota Bharu, Kelantan
- Universiti Malaysia Kelantan, Bachok Campus, Kelantan
- Wad Forensik Hospital Bahagia Ulu Kinta, Ipoh, Perak
- Cadangan Mendirikan Sebuah Klinik Kesihatan Taiping – 2 Tingkat (Jenis KK2) Di Atas Lot 2089, Jalan Tupai, Mukim Tupai, Daerah Larut & Matang, Perak Darul Ridzuan
- Tasik Raban Resort, Lenggong, Perak
- Cadangan Rekabentuk Sistem Saliran bagi Sekolah Kebangsaan Pendang 2, Bandar Pendang, Daerah Pendang, Kedah
- Kolej Sains Kesihatan Bersekutu Johor, Johor Bahru
- Mahkamah Piawai Dua Bilik Bicara at Alor Gajah
- Bangunan Gunasama Persekutuan Klang, Selangor
- Membina kolam tadahan banjir di Taman Perpaduan, Ipoh, Perak
- Cadangan Membina Kolam Tadahan di Taman Putra Impian, Bercham, Ipoh, Perak.
- Kwasa Damansara New Township Development
- Cadangan Pelan Induk Pembangunan Kwasa Damansara
- Cadangan Menaiktaraf Sistem Saliran Air Bawah Tanah Di Padang Astaka Utara
- Cadangan Menaiktaraf Padang Permainan di SK Francis Light, Georgetown, Pulau Pinang
- Cadangan Pembinaan Ibu Pejabat Polis Daerah (IPD) Pasir Mas Di Atas Lot 1155 Mukim Gua Daerah Pasir Mas, Kelantan Darul Naim.
- UMT- Kompleks Pendidikan Dan Pembangunan Insaniah, Terengganu
- Pusat Latihan Jabatan Pertahanan Awam (JPAM) Kluang, Johor.
- Cadangan Mendirikan Sebuah Klinik Kesihatan Jenis 2 Bandar Perda Di Atas PT 2959, Mukim 06, Daerah Seberang Perai Tengah,Pulau Pinang
LIST OF VISITORS
The Bio-ecological Drainage System (BIOECODS) at Engineering Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) in Nibong Tebal, Penang, attracts a diverse range of visitors. These visitors include representatives from government agencies, educational institutions, schools, NGO's and private organisations, as well as individuals from local and international communities. Guided tours and interactive presentations provide insights into the efficacy of eco-friendly drainage systems in effectively managing stormwater, reducing urban flooding, improving water quality, and enhancing biodiversity.
Materials related to BIOECODS:
Journal/Conference Proceeding
- Characteristic of Stormwater Quality Using BIOECODS in JKR Pilot Projects
- Bio‐ecological drainage system (BIOECODS) for water quantity and quality control
- BIO-ECOLOGICAL DRAINAGE SYSTEM (BIOECODS): CONCEPT, DESIGN AND CONSTRUCTION
- Storm water treatment using Bio‐Ecological Drainage System
- Stormwater Purification Capabilty of BIOECODS
- Peak Flow Attenuation using Ecological Swale and Dry Pond
- Advances and Challenging Issues in Subsurface Drainage Module Technology and BIOECODS: A Review
- Sustainable Urban Drainage System (SUDS) – Malaysian Experiences
- Water balance: Case study of a constructed wetland as part of the bio-ecological drainage system (BIOECODS)
- Assessing phytoplankton distribution and water quality in constructed wetlands during dry and wet periods: A Case Study in USM Engineering Campus
- Biodiversity in stormwater constructed wetlands: Case study of USM Wetland
Guidelines

Other Article:
Newspaper Cutting
- https://redac.eng.usm.my/images/Download/BeritaKampus2009.jpg
- https://redac.eng.usm.my/images/Download/Utusan_Malaysia_050_February_2003.jpg (Utusan Malaysia, February 2003)
- https://redac.eng.usm.my/images/Download/Utusan%20Malaysia%2001%20February%202003.jpg (Utusan Malaysia, 1 February 2003)
- https://redac.eng.usm.my/images/Download/Utusan%20Malaysia%2029%20January%202000.jpg (Utusan Malaysia, 29 January 2020)
- https://redac.eng.usm.my/images/Download/Berita%20Harian%204%20Julai%202000.jpg (Berita Harian, 4 July 2002)
- https://redac.eng.usm.my/images/Download/thesun%2015%20Disember%202000.jpg (The Sun, 15 December 2000)
- https://redac.eng.usm.my/images/Download/nst%2015%20Dec%202000.jpg (New Strait Times, 15 December 2000)
- https://redac.eng.usm.my/images/Download/nst%2005%20July%202000.jpg (New Strait Times, 5 July 2000)
- https://redac.eng.usm.my/images/Download/Harian%20metro%2029mei2001.jpg (Harian Metro, 29 May 2001)
- https://redac.eng.usm.my/images/Download/star%2005%20Feb%202003.jpg (The Star, 15 February 2003)
Videos
Visitors visit the National Pilot Project, BIOECODS located at the Engineering Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM Engineering Campus)
Implementation of BIOECODS at the New Township of Kwasa Damansara



